posted by Dongwoo Kim
Relational knowledge graphs formalise our understanding about the world and help us reason and infer in a wide range of tasks. The construction of a knowledge graph is an active research area with many important and challenging research questions. Throughout this research, we address some important problems in the knowledge graph construction and propose novel statistical relational models to solve the problems.
The problem
Knowledge base construction consists of two tasks: extracting information from external sources, and inferring missing information through a statistical analysis on the extracted information. Several methods have been proposed to extract information from external sources. In many domains, however, there are not enough external sources to extract information, and consequently, the statistical analysis did not work properly. An incremental knowledge population through human experts can help to reduce the gap between the statistical analysis and information extraction.
Our Solution
In our work, we address these challenges as follows:
- We propose a probabilistic formulation of bilinear tensor factorisation that allows us to predict the uncertainty of unobserved triples.
- We incorporate the graph path structure of a knowledge graph into the proposed factorisation by modelling a composition of relations as algebraic operations in the probabilistic embedding space.
- We propose an incremental knowledge population method that searches the factorised space, trading of exploration and exploitation using Thompson sampling.
- Experiments on the knowledge completion with three real-world datasets show that the compositional model predicts unseen triples better than the bilinear factorisation model.
- Experiments show the importance of uncertainty in the incremental knowledge base population task. The better predictive model does not guarantee a better knowledge population due to an improper uncertainty measure.
Sample results
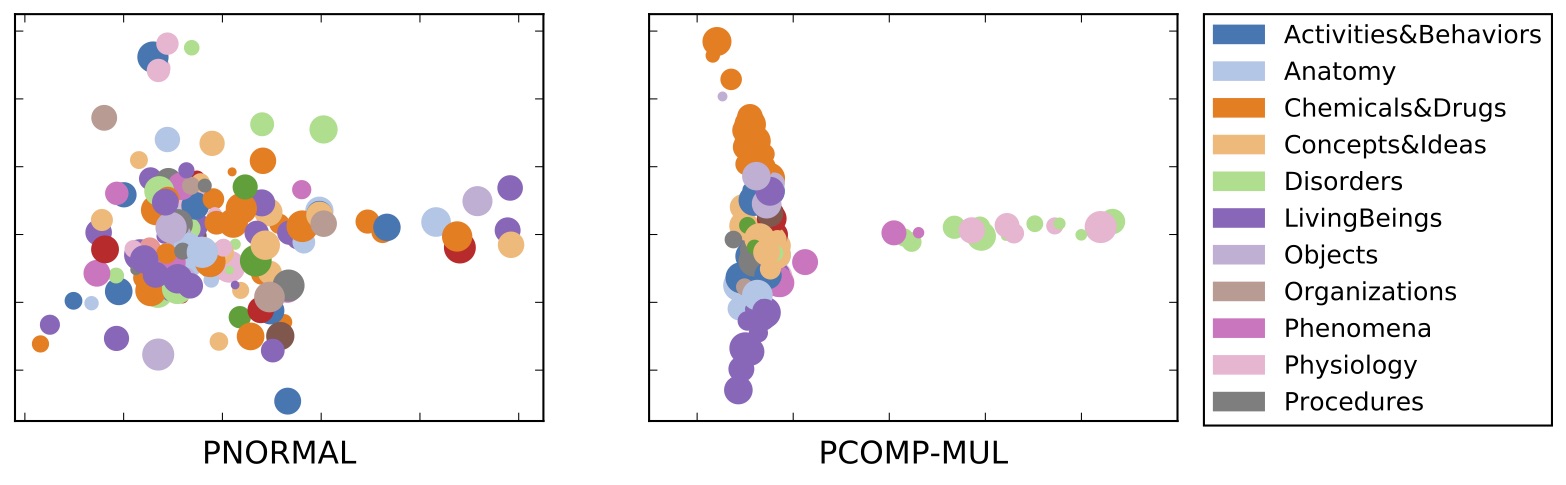
Embedding learned entities of the UMLS dataset into a two-dimensional space through the spectral clustering. Entities with the same type are represented by the same color. The entities with the same type are located closer to each other with PCOMP-MUL (a compositional model) than PNORMAL (a non-compositional model).
Resources
Dongwoo Kim, Lexing Xie, Cheng Soon Ong, Probabilistic Knowledge Graph Construction: Compositional and Incremental Approaches, in Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM ‘16), Indianapolis, IN, USA.
| Download: | Paper + SI |
| Presentation | Slides |
| Poster | Poster |
| Data: | Data |
| Bibtex: |
@inproceedings{kim2016,
title = {{Probabilistic Knowledge Graph Construction: Compositional and Incremental Approaches}},
author = {Kim, Dongwoo and Xie, Lexing and Ong, Cheng Soon},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management},
series = {CIKM '16},
address = {Indianapolis, IN, USA},
doi = {10.1145/2983323.2983677},
keywords = {Knowledge graph, active learning, Thompson sampling},
year = {2016}
}